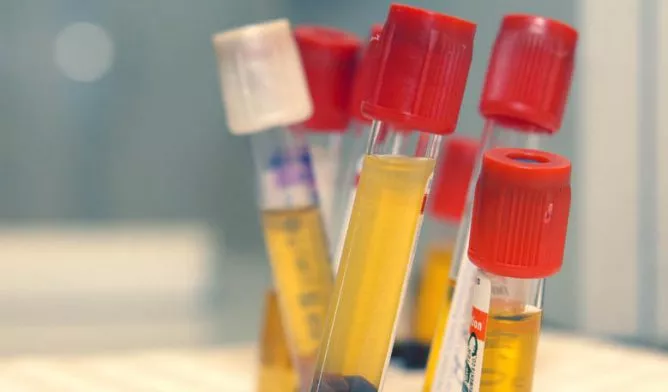
serum
Serum refers to the light yellow transparent liquid separated from the fibrinogen after blood coagulation, or refers to the plasma from which fibrin has been removed.
Its main role is to provide basic nutrients, provide hormones and various growth factors, provide binding proteins, provide contact-promoting and stretch factors to make cells adhere to the wall from mechanical damage, and to protect cells in culture.
The main components of serum
Serum is a very complex mixture formed by removing fibrinogen from plasma. Although most of its components are known, some of them are still unclear. The composition and content of serum often vary with the sex, age, and physiology of the blood supply animal. Conditions and nutritional conditions vary.
Serum is a colloidal liquid without fibrinogen in plasma, which has the functions of maintaining the normal viscosity, pH and osmotic pressure of blood.
It is mainly composed of water and various chemical components, including albumin, α1, α2, β, γ-globulin, triglycerides, total cholesterol, alanine aminotransferase and so on.
Serum contains various plasma proteins, peptides, fats, carbohydrates, growth factors, hormones, inorganic substances, etc. These substances have a physiological balance to promote cell growth or inhibit growth activity.
Method of preserving serum
Serum should be stored at -5°C to -20°C. If stored at 4°C, do not exceed one month. If you can’t use up one bottle at a time, it is recommended to pack the aseptic serum into an appropriate sterilized container, and then put it back into the freezer.
How to thaw the serum without compromising the quality of the product?
After taking the serum out of the freezer, first dissolve it in a refrigerator at 2-8°C, and then dissolve it completely at room temperature. But it must be noted that during the dissolution process must be shaken regularly and evenly
How to avoid the formation of sediment?
1. When thawing the serum, please follow the recommended gradual thawing method (-20°C to 4°C to room temperature). If the temperature changes too much when the serum is thawed (such as -20°C to 37°C), the experiment shows Very easy to produce sediment.
2. When thawing the serum, please shake it evenly at any time to make the temperature and composition uniform and reduce the occurrence of precipitation
3. Do not leave the serum at 37°C for too long. If placed at 37°C for too long, the serum will become turbid, and many more unstable components in the serum will also be damaged, which will affect the quality of the serum.
4. The heat inactivation of serum is very easy to cause the increase of sediment. If it is not necessary, this step is not necessary.
The difference between serum, plasma and whole blood
All blood after anticoagulation treatment is whole blood; the light yellow liquid obtained after centrifugation to remove blood cells is plasma.
If the blood is not subjected to anticoagulation treatment and allowed to coagulate on its own, the blood will automatically coagulate under the action of a series of coagulation factors within a period of time after the blood is drawn. The blood will first coagulate into a whole, and then after a period of time or use Centrifuge centrifuge, the coagulated part of the blood will be separated from some clear light yellow liquid, these liquids are called serum.
Serum and plasma seem to be the same on the surface, but the main difference is that the serum does not contain fibrinogen, which is obtained after blood coagulation without anticoagulation treatment.
When taking blood for laboratory tests, it is often encountered that certain laboratory tests require serum determination, whole blood determination, and plasma determination, which refer to the three main processing methods and requirements of blood samples.